Wireless Industrial Sensors: A Complete Guide to Technology, Types, and Applications
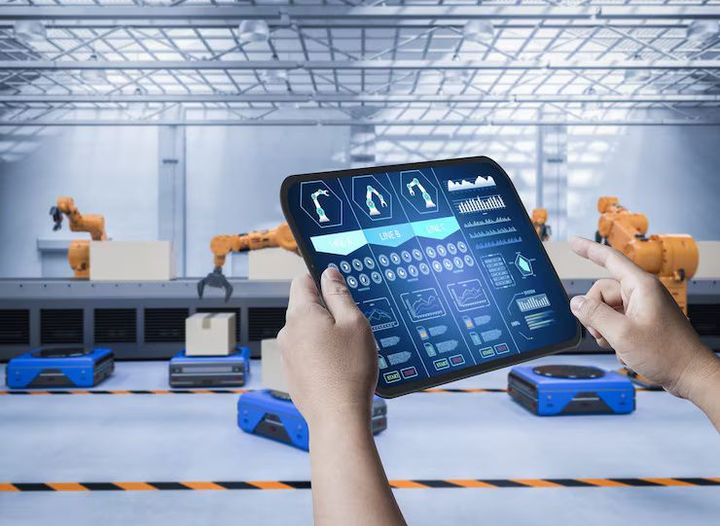
Wireless industrial sensors are devices used in modern manufacturing and industrial environments to monitor, measure, and transmit critical operational data without relying on wired connections. These sensors detect parameters such as temperature, pressure, vibration, humidity, and motion and send information to control systems for analysis and action
The concept of wireless sensing emerged from the need to reduce complex cabling, improve installation flexibility, and enable real-time data collection in harsh or remote industrial environments. Traditional wired sensors were limited by installation costs, maintenance challenges, and inflexibility.
Today, wireless industrial sensors form the backbone of Industry 4.0, smart factories, and predictive maintenance strategies. By enabling seamless communication between machines, systems, and operators, they enhance operational efficiency, safety, and decision-making.
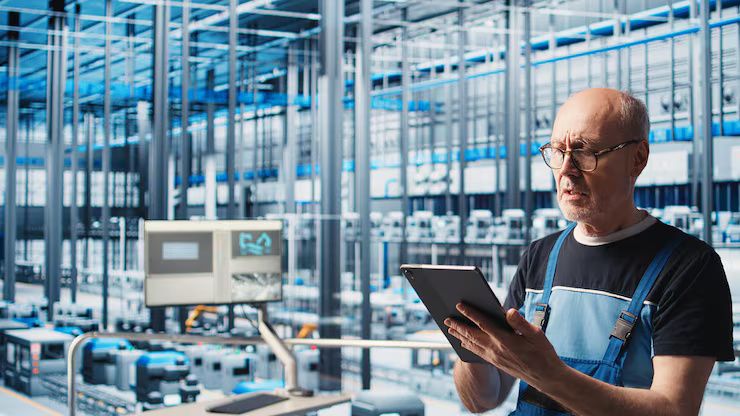

Importance — Why Wireless Industrial Sensors Matter Today
Wireless industrial sensors play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, energy management, logistics, and industrial automation. Their significance stems from the following factors:
• Real-Time Monitoring
Sensors provide continuous data on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and production processes, enabling timely interventions.
• Reduced Installation Complexity
Without extensive cabling, installation is faster and less disruptive. Wireless networks are easier to scale as production lines evolve.
• Predictive Maintenance
By monitoring vibration, temperature, and other parameters, sensors detect potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime.
• Safety Enhancements
Sensors monitor hazardous conditions, ensuring worker safety in environments like chemical plants, refineries, and heavy machinery facilities.
• Energy Efficiency
Monitoring energy consumption helps industries optimize power use, reduce waste, and achieve sustainability goals.
• Integration with Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Wireless sensors connect seamlessly with cloud platforms, analytics systems, and AI algorithms, forming the foundation of smart manufacturing ecosystems.
Industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to pharmaceuticals, oil and gas, and food processing benefit from the operational insights and cost efficiencies provided by wireless industrial sensors.
Recent Updates — Trends and Innovations (2024–2025)
The last year has seen advancements in wireless sensor technology driven by IoT adoption, AI integration, and industrial digitalization.
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| IoT-Enabled Sensors | Sensors now integrate directly with cloud platforms and IoT protocols like MQTT and OPC UA. | Real-time monitoring and remote control improve decision-making. |
| Edge Computing Integration | Data processing is partially handled locally at the sensor or gateway. | Reduces latency and network congestion, enabling faster response times. |
| Energy-Harvesting Sensors | Sensors powered by ambient energy sources (vibration, thermal, or solar). | Minimizes battery replacements and maintenance costs. |
| Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN) | Adoption of technologies like LoRaWAN and NB-IoT for long-range, low-power communication. | Extends sensor coverage in large industrial sites. |
| AI and Predictive Analytics | Machine learning algorithms analyze sensor data to detect anomalies. | Enhances predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. |
Additionally, smart manufacturing plants in 2024–2025 have increasingly deployed wireless vibration sensors, temperature monitors, and energy meters to track equipment performance, reduce unplanned downtime, and improve supply chain visibility.
Laws or Policies — Regulations Affecting Wireless Industrial Sensors
Wireless industrial sensors operate within regulated frameworks to ensure safety, electromagnetic compliance, and data security. Regulations differ by country but typically include:
Electrical and Wireless Standards
-
IEC 61000 – Electromagnetic compatibility standards for industrial devices.
-
FCC regulations (USA) – Ensures wireless devices do not interfere with other communication channels.
-
ETSI (Europe) – Defines wireless spectrum usage for industrial applications.
Safety Standards
-
ISO 13849 – Functional safety of machinery.
-
IEC 61508 – Safety-related electrical/electronic systems in industrial contexts.
Data Security and Privacy
-
Industrial sensors transmitting sensitive operational data must follow cybersecurity standards (NIST, ISO/IEC 27001) to prevent breaches and ensure compliance.
Environmental and Operational Standards
-
Sensors must withstand temperature extremes, moisture, dust, and vibration according to IP ratings (Ingress Protection).
-
Some industries, such as pharmaceuticals or food processing, require sensors to comply with HACCP or GMP standards.
Compliance ensures reliable operation, reduces risks of malfunction, and aligns industrial automation systems with international best practices.
Tools and Resources — Applications and Support Systems
Wireless industrial sensors are integrated into broader industrial networks and supported by software tools for monitoring, data analysis, and maintenance.
Industrial IoT Platforms
-
Provide centralized dashboards for real-time sensor data visualization.
-
Examples include Siemens MindSphere, PTC ThingWorx, and AWS IoT.
Predictive Maintenance Software
-
Uses sensor data to predict equipment failure and schedule proactive maintenance.
-
Reduces downtime and extends machine lifespan.
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
-
Gateways and hubs connect multiple sensors, aggregate data, and transmit to control systems.
Calibration and Testing Tools
-
Ensure sensors remain accurate over time.
-
Include multi-parameter calibrators, signal analyzers, and vibration testers.
Communication Protocol Tools
-
Software for LPWAN, Zigbee, BLE, and 5G networks helps configure and maintain connectivity.
Data Analytics and Visualization Tools
-
Analyze historical and real-time sensor readings for trend analysis and operational insights.
-
Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and custom dashboards are commonly used.
These tools allow industries to monitor production, energy, and environmental conditions more effectively, contributing to optimized operations.
Types of Wireless Industrial Sensors
Wireless industrial sensors are categorized based on the parameter they monitor:
Temperature Sensors – Measure heat in processes or equipment.
Pressure Sensors – Monitor fluid or gas pressure in pipelines.
Vibration Sensors – Detect mechanical anomalies in rotating or moving machinery.
Proximity Sensors – Identify object presence or distance in automated assembly.
Flow Sensors – Track liquid or gas flow in industrial systems.
Level Sensors – Measure liquids or solids in tanks and silos.
Environmental Sensors – Monitor humidity, air quality, and light for workplace and equipment safety.
Each type plays a critical role in operational monitoring, safety assurance, and smart automation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are wireless industrial sensors used for?
They monitor operational parameters like temperature, pressure, vibration, and motion, providing data for predictive maintenance, process optimization, and safety management.
2. How do wireless sensors differ from wired sensors?
Wireless sensors transmit data without physical cables, simplifying installation, reducing maintenance costs, and enabling flexible deployment in harsh or complex industrial environments.
3. Can wireless sensors work in extreme industrial conditions?
Yes. Most industrial-grade sensors are designed to withstand heat, dust, vibration, and moisture, often with IP67 or higher ratings for protection.
4. Are wireless sensors compatible with Industry 4.0 systems?
Yes. They integrate with Industrial IoT platforms, edge computing systems, and predictive analytics, forming the foundation of smart manufacturing ecosystems.
5. How is data security maintained in wireless industrial sensors?
Data is secured using encryption protocols, authentication mechanisms, and compliance with cybersecurity standards like ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST guidelines.
Conclusion
Wireless industrial sensors are pivotal in modern manufacturing, industrial automation, and smart factory development. By enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and operational efficiency, they help industries reduce costs, improve safety, and optimize performance.
Technological advancements such as IoT integration, edge computing, energy harvesting, and AI analytics continue to enhance sensor capabilities. Regulatory standards and data security frameworks ensure reliable, safe, and compliant industrial operations.