X-Ray Machines: A Complete Guide to Technology, Types, and Applications
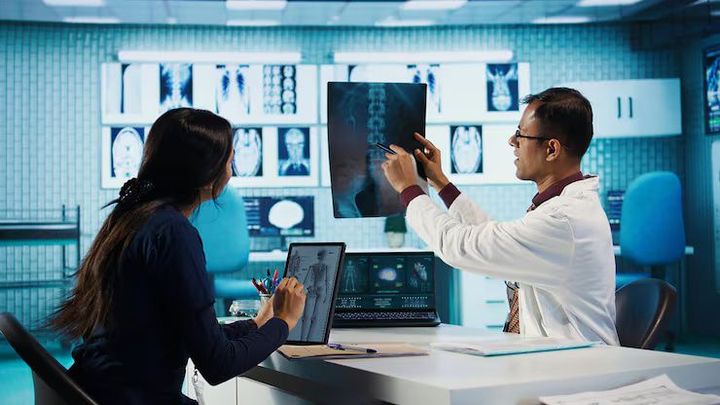
X-ray machines are imaging devices that use electromagnetic radiation to visualize internal structures of objects or the human body. Introduced in the late 19th century after Wilhelm Röntgen’s discovery of X-rays in 1895, these machines changed how health and industrial sectors understand hidden structures without damaging the material being studied
The idea behind X-ray imaging is simple yet transformative. When X-rays pass through objects, different materials absorb the rays at different rates. Dense structures like bones absorb more radiation, appearing white on scans, while softer tissues appear darker. This contrast helps doctors diagnose fractures, infections, and diseases.
Importance — Why X-Ray Machines Matter Today
X-ray machines are essential across multiple fields because they offer a fast, non-invasive way to examine internal structures. Their importance has increased significantly as industries and healthcare rely on precise imaging for analysis, safety, and decision-making.
Key reasons why X-ray machines matter today:
Medical Diagnostics
X-rays enable healthcare professionals to identify conditions such as fractures, lung infections, dental issues, joint problems, and digestive blockages. Early detection supports timely treatment and reduces complications.
Industrial Quality Control
Manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and construction industries use X-ray systems for non-destructive testing. These scans detect cracks, voids, weld flaws, and structural abnormalities without damaging components.
Security and Safety
Airports, government buildings, and commercial checkpoints rely on X-ray scanners to inspect bags, parcels, and cargo. These machines help identify prohibited items, improving public security systems.
Research and Scientific Study
X-ray diffraction and crystallography support studies in chemistry, pharmaceuticals, materials science, and nanotechnology. They reveal molecular structures and help develop new scientific innovations.
Efficiency and Accuracy
Modern digital X-ray machines deliver real-time imaging, improve clarity, and store results electronically. This reduces process time and enhances diagnostic confidence across sectors.
As industries transition to digital ecosystems, X-ray machines are becoming more integrated with software, automation, and cloud platforms for enhanced performance and data management.
Recent Updates — Trends and Developments (2024–2025)
In recent years, digital technology and automation have significantly influenced the evolution of X-ray machines. Several major updates have shaped how these machines are used in healthcare, industrial testing, and security screening.
Here are key developments from 2024–2025:
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Radiography (DR) | Transition from film-based to digital sensors. | Faster imaging, better resolution, lower radiation. |
| AI-Powered Imaging | Artificial intelligence assists in detecting abnormalities in scans. | Enhances diagnosis accuracy in medical and industrial settings. |
| Portable and Mobile X-Ray Units | Compact devices for remote clinics and field inspections. | Expands accessibility and supports emergency use. |
| Low-Dose Radiation Technology | Innovations reduce exposure while maintaining clarity. | Improves patient and operator safety. |
| 3D Imaging and Tomosynthesis | Layered imaging for better structural visualization. | Provides more detailed analysis of tissues and materials. |
| Automated Security Scanners | Advanced baggage scanners using AI pattern detection. | Enhances safety at airports and high-traffic venues. |
In 2025, the global focus is on automation, safety optimization, and integration of artificial intelligence into X-ray systems. These advancements make machines easier to use and more reliable across various applications.
Laws and Policies — Regulations for X-Ray Machines
X-ray machines are strictly regulated worldwide because they involve radiation, which must be controlled for safety. Regulations ensure proper device design, safe operation, and regular monitoring.
Key Regulations in India
-
Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB): Governs installation, licensing, and operation of all radiation-emitting equipment.
-
Radiation Protection Rules (2004): Defines safety requirements for shielding, operator protection, and periodic inspections.
-
Digital Health Guidelines: Encourage safe adoption of digital radiography systems in healthcare environments.
-
Workplace Safety Standards: Ensure that operators and patients have controlled exposure within permissible limits.
International Regulations
-
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection): Sets global radiation safety standards.
-
FDA (USA): Regulates design and performance of X-ray medical devices.
-
CE Certification (Europe): Ensures compliance with safety and manufacturing standards.
-
IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency): Provides guidelines for radiation protection and equipment usage.
These standards ensure that X-ray machines are safe, reliable, and responsibly operated across medical, industrial, and security sectors.
Tools and Resources — Helpful Systems for X-Ray Operations
Various tools, software, and platforms support the operation, analysis, and management of X-ray machines. These resources help improve safety, accuracy, workflow, and documentation.
Key Tools and Resources
Imaging Software
-
Digital radiography viewers
-
3D reconstruction software
-
Automated defect detection programs for industrial testing
Radiation Monitoring Tools
-
Personal dosimeters
-
Area radiation monitors
-
Shielding assessment software
Operational Management Systems
-
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems)
-
Cloud-based image storage platforms
-
Workflow automation tools for medical imaging
Industrial Inspection Resources
-
Non-destructive testing (NDT) analysis software
-
Portable inspection toolkits
-
Automated scanning frameworks for quality control
Safety and Compliance Resources
-
AERB e-lincensing portals (India)
-
Global radiation safety guidelines
-
Regular safety audit templates
These resources help maintain precision, ensure safety, and support long-term equipment performance.
FAQs — Common Questions About X-Ray Machines
1. How does an X-ray machine work?
X-rays pass through objects, and different materials absorb the radiation at different levels. A detector captures this energy and forms an image based on the absorption patterns.
2. Are X-ray machines safe?
Modern X-ray machines use low-dose radiation and follow strict safety standards. When operated correctly, exposure remains within globally accepted limits.
3. What are the main uses of X-ray machines?
X-ray machines are used in medical imaging, industrial defect detection, security screening, and scientific research.
4. What is digital radiography?
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with digital detectors, allowing faster imaging, higher clarity, and easier storage.
5. Do X-ray machines require regulation?
Yes. Radiation-emitting machines are regulated to ensure safe use. Licensing, inspections, and radiation monitoring are mandatory in most countries.
Conclusion
X-ray machines remain one of the most important inventions in modern science, supporting healthcare, industry, and security with accurate and non-invasive imaging. Their evolution from early film-based systems to advanced digital and AI-enhanced technologies has transformed diagnostics and inspection capabilities worldwide.





